Understanding Google Search Console’s INP Metric
In the vast landscape of digital marketing, search engine optimization (SEO) stands as a crucial pillar for businesses aiming to enhance their online presence and visibility. Within the realm of SEO, Google Search Console emerges as an indispensable tool, offering valuable insights and metrics to optimize website performance. Among these metrics, one that has gained significant attention is the “Input Timing” or INP (Interaction to Next Paint) metric, which is the newest one. In this blog, we delve deep into understanding the new INP metric in the Google Search Console, its significance, and how to leverage it effectively to enhance your website’s performance.

Introduction to Google Search Console and Its Metrics
Google Search Console, formerly known as Google Webmaster Tools, is a free service provided by Google that helps website owners monitor, maintain, and troubleshoot their site’s presence in Google search results. It offers a plethora of tools and reports to analyze various aspects of a website’s performance, such as indexing status, search queries, crawl errors, and more.
One of the most critical aspects of the Google Search Console is its ability to provide insights into how Google perceives and interacts with your website. This includes metrics related to user experience, site speed, mobile friendliness, and more. Among these metrics, Interaction to Next Paint (INP) plays a vital role in evaluating the user experience, particularly on mobile devices.
Understanding the INP (Interaction to Next Paint) Metric
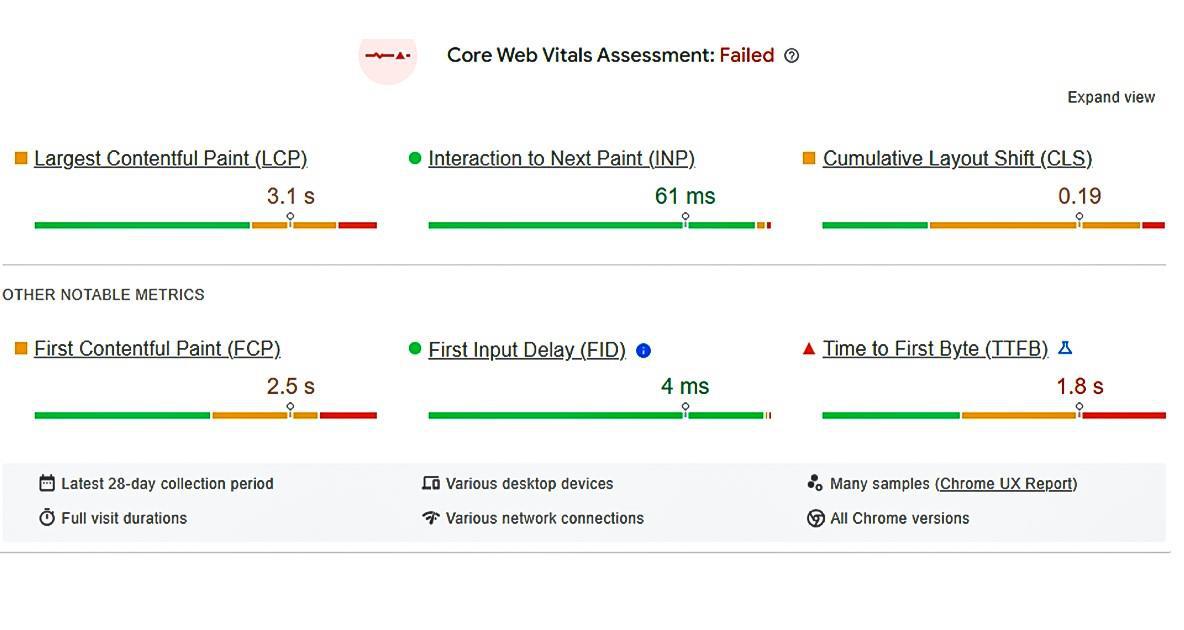
INP, or Input Timing, is a metric introduced by Google to measure the responsiveness of a web page to user input events, such as tapping or clicking. It specifically focuses on the time taken by a web page to respond to user interactions, particularly on mobile devices. INP is a crucial component of Core Web Vitals, a set of user-centered metrics that Google uses to assess the overall user experience of a webpage.
As of March 12, 2024, Google made significant changes to its Core Web Vitals set, shifting from First Input Delay to Interaction to Next Paint. With this change, a new metric becomes one of Google’s ranking factors, emphasizing the importance of optimizing website performance to maintain or improve organic search visibility. This shift underscores the significance of monitoring and optimizing the INP metric, as it directly influences user experience and subsequently impacts search engine rankings.
The INP metric primarily measures two key aspects:
First Input Delay (FID): FID measures the time from when a user first interacts with a page (e.g., clicks a button, or taps on a link) to the time when the browser is able to respond to that interaction. It quantifies the responsiveness of a webpage and is particularly relevant for pages with interactive elements.
Total Blocking Time (TBT): TBT measures the total amount of time between First Contentful Paint (FCP) and Time to Interactive (TTI), where the main thread is blocked for more than 50 milliseconds. In simpler terms, it represents the duration during which the page is unresponsive to user input.
Both FID and TBT are critical factors in determining the overall user experience of a webpage, especially on mobile devices, where performance can significantly impact user satisfaction and engagement.
Significance of the INP Metric in SEO
The INP metric holds immense significance in the realm of SEO for several reasons:
User Experience (UX) Optimization: User experience is a crucial ranking factor for Google, and INP directly influences the perceived responsiveness and interactivity of a webpage. By optimizing INP, webmasters can enhance the overall UX, leading to improved rankings and user engagement.
Core Web Vitals and Page Experience Update: Google has incorporated Core Web Vitals, including INP, into its ranking algorithm as part of the Page Experience update. Websites that provide a seamless and responsive user experience are more likely to rank higher in search results, making INP optimization essential for Search Engine Optimization success.
Mobile-First Indexing: With the increasing prevalence of mobile browsing, Google has shifted to mobile-first indexing, meaning it primarily uses the mobile version of a webpage for indexing and ranking. As INP directly impacts the mobile user experience, optimizing this metric is crucial for maintaining visibility in mobile search results.
Competitive Advantage: Websites that prioritize INP optimization gain a competitive edge by delivering faster, more responsive experiences to users. This can result in lower bounce rates, higher conversion rates, and ultimately better performance in search engine rankings compared to competitors with poor INP scores.
How to Improve the INP Metric
Optimizing the INP metric requires a combination of technical optimizations and best practices aimed at enhancing website performance and responsiveness. Here are some strategies to improve your website’s INP score:
Minimize JavaScript Execution: Excessive JavaScript execution can lead to delays in response to user input. Minimize and optimize JavaScript code, prioritize critical scripts, and defer non-essential scripts to improve FID and reduce TBT.
Optimize Server Response Time: Ensure fast server response times by leveraging caching mechanisms, optimizing server configurations, and using content delivery networks (CDNs) to deliver content efficiently to users.
Prioritize the Critical Rendering Path: Streamline the critical rendering path by optimizing CSS delivery, reducing render-blocking resources, and ensuring efficient resource loading to accelerate the initial page rendering process.
Eliminate Render-Blocking Resources: Identify and eliminate render-blocking resources, such as CSS and JavaScript files, that delay the rendering of the webpage and hinder user interaction.
Use Browser Caching and Compression: Leverage browser caching and compression techniques to reduce the time required to fetch and render resources, improving overall page load times and responsiveness.
Optimize Images and Media: Compress and optimize images and multimedia content to reduce their file size without compromising quality, thereby minimizing load times and improving overall page responsiveness.
Implement Lazy Loading: Implement lazy loading for images, videos, and other non-critical resources to defer their loading until they are needed, reducing the initial page load time and improving TBT.
Monitor and Iterate: Regularly monitor INP metrics through Google Search Console and other performance monitoring tools. Identify bottlenecks and areas for improvement, and iteratively refine your website design to optimize input performance continually.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Google Search Console’s INP (Interaction to Next Paint) metric is now playing a pivotal role in evaluating the responsiveness and user experience of web pages, particularly on mobile devices. By understanding the significance of INP and implementing optimization strategies, website owners can enhance their site’s performance, improve rankings in search results, and provide users with faster, more seamless experiences. As Google continues to prioritize user experience as a key ranking factor, optimizing INP is essential for maintaining competitiveness and driving success in the ever-evolving landscape of SEO.
